
 |
The database tries to collect all published astrophysical information of interesting objects listed by their type, which could be possible secondary targets for space missions such as MOST (http://www.astro.ubc.ca/MOST) or COROT (http://www.astrsp-mrs.fr/projets/corot/pagecorot.html).
Several catalogs representing different types of objects - such as delta Scuti stars, rapidly oscillating Ap stars etc. - are included.
The data are collected from different sources (publications and private communication) and will be updated regularly. A list of references is given at the References Page:
Catalogs to be included:
The database was created using PostgreSQL and PHP.
 PostgreSQL is a sophisticated open-source database management system available for many operational systems.
(http://www.postgresql.org)
PostgreSQL is a sophisticated open-source database management system available for many operational systems.
(http://www.postgresql.org)
PHP is a server-side, cross-platform, HTML embedded scripting language.
(http://www.php.net)

4.1. New user:
At the main page you are asked to register if you are a new user. Follow the link and fill out the form carefully. If the automatic registration was successful, you will be asked to login now.
4.2. Login and Password:
If you have already registered please give your login and password to enter the database!
If you forgot your password, please contact the administrator.
If you log into the database a session ID will be assigned; it expires after 30 minutes. You will then be asked to login again.
There are four options between it is required to choose:
5.1. Object Search:
To search for a specific object an identifier has to be given. The following identifiers can be used:
A list of all available information for this object will be given.
To find all objects of one or more types in a given magnitude and/or right ascension and/or declination range specify in which catalogs the query should be performed: click on the name(s) of the catalog(s) in the scroll-down menu. (To submit a query to all catalogs select the corresponding entry!)
You also have to define at least one limit for one of the criteria, say a lower limit for the magnitude, to retrieve the available information.
Note: Searching the database using the right ascension as criterion is only permitted if a lower and an upper limit is defined!
Example for the Parameter Search Input:
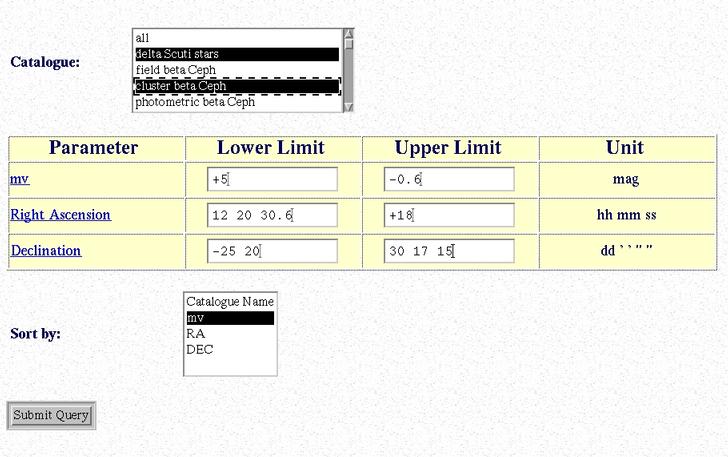
The output of this search lists all objects matching the given criteria with their positions in equatorial coordinates (2000.0) and magnitudes. For detailed information on a certain object click on the button  next to the object name.
next to the object name.
In case of a multiple entry of one object it is listed separately for each catalog with the astrophysical information available accordingly.
5.3. Field Search:
To perform the Field Search please choose a catalogue and enter coordinates and a radius in arcminutes!
Per default the output format will be HTML allowing you to retrieve a list of objects with their positions in equatorial coordinates (2000.0), magnitudes and the distance from the main coordinates you specified before in arcminutes. Like in the Parameter Search you can click on the button  next to
the object name to display all available information.
next to
the object name to display all available information.
If you select ASCII as output format you will get just a plain list of the objects (characterized by name, right ascension, declination, V magnitude and the radius from the target specified before), which will allow you to store the information easier in a text-file for further usage.
5.4. COROT and MOST Field of View Masks:
At the query result of the the Object Search one can choose between the COROT and MOST Field of View Masks by clicking one the according button in the top of the page.
5.4.1. COROT Masks:
The COROT Mask consists of 4 2k CCD's where one CCD images 1.27 x 1.27 degree of the sky. The dispatching (left or right pair of CCD's) of the Exoplanet and the Seismology Fields depend on the observed sky region. The Mask tool queries the database within a radius of 4 degree and plots the CCD Mask over the result.
First the Target star is aligned to the upper-left or lower-right center of the Seismology Field. With the RA (in min) and DEC offset (in arcmin) adjustment the Mask can be shift in x and y axis. The Rotation angle (in degree) let the Mask rotate around the center of the 4 CCD's. The #star brightest stars are sorted and numbered by brightness and listed in the result.
5.4.2. MOST Masks:
The MOST Mask consists of a 1k CCD which images 53 x 53 arcminutes of the sky and an array of 36 Fabry lenses which projects the Primary Target as a defocused ring on the CCD.
With the Fabry lens adjustment the position of the Primary Target on the CCD can be choosen. The Fabry lenses are numbered line by line from the upper left to the lower right corner. The Rotation angle (in degree) let the Mask rotate around the choosen Fabry lens. The 42 brightest stars are sorted and numbered by brightness and listed in the legend.
| This database is created designed and maintained by A. Kaiser, Th. Kallinger, P. Mittermayer and K. Zwintz from the Institute for Astronomy, University Vienna, Austria. For any problems please contact the administrator |


|